Dive into the fascinating world of POGIL Cell Cycle Regulation Answers, where we explore the intricate mechanisms that govern cellular growth and division. This comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of cell cycle regulation, empowering you with a deeper understanding of this fundamental biological process.
POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) activities provide an interactive and engaging approach to learning about cell cycle regulation. These activities foster critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a profound grasp of the subject matter.
Cell Cycle Regulation Overview: Pogil Cell Cycle Regulation Answers
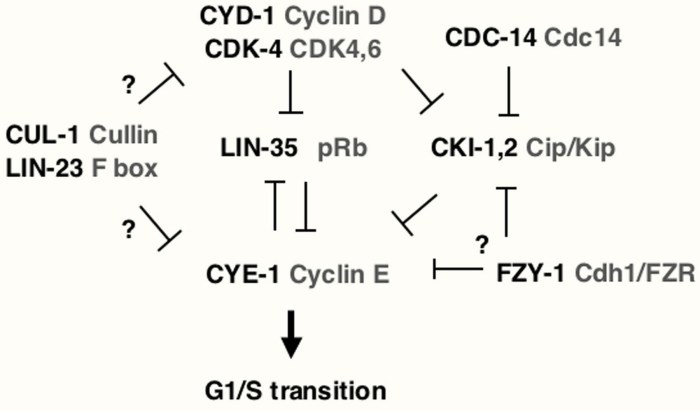
Cell cycle regulation is the intricate process by which eukaryotic cells control their progression through the various stages of the cell cycle. It ensures the orderly progression of events, including DNA replication, chromosome segregation, and cell division, to maintain genomic integrity and proper cellular function.
The importance of cell cycle regulation cannot be overstated. Dysregulation of the cell cycle can lead to genomic instability, aneuploidy, and uncontrolled cell proliferation, which are hallmarks of cancer and other diseases.
Key Components Involved in Cell Cycle Regulation
The regulation of the cell cycle is a complex and highly orchestrated process involving numerous proteins and molecular mechanisms. Key components include:
- Cyclins: Regulatory proteins that bind to and activate cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs).
- Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs): Enzymes that phosphorylate target proteins, driving the progression of the cell cycle.
- Checkpoint proteins: Molecules that monitor the fidelity of DNA replication and cell division, ensuring that critical events occur correctly.
- Transcription factors: Proteins that regulate gene expression, controlling the production of proteins involved in cell cycle progression.
POGIL Cell Cycle Regulation Activities

Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL) is an effective pedagogical approach that engages students in active learning and critical thinking. It provides a structured environment where students work in small groups to investigate scientific concepts and develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
POGIL activities are particularly well-suited for teaching cell cycle regulation, a complex and dynamic process that involves multiple checkpoints and regulatory mechanisms.
POGIL activities for cell cycle regulation typically involve students working through a series of guided questions and activities that help them to:
- Identify the different phases of the cell cycle and their key events.
- Understand the role of checkpoints in regulating the cell cycle.
- Explore the mechanisms that control cell cycle progression.
- Analyze data and draw conclusions about the regulation of the cell cycle.
POGIL activities can be used to teach cell cycle regulation in a variety of ways. For example, students can work through a POGIL activity to:
- Create a model of the cell cycle that illustrates the different phases and checkpoints.
- Analyze data from a cell cycle experiment to identify the factors that affect cell cycle progression.
- Design an experiment to test a hypothesis about the regulation of the cell cycle.
POGIL activities are a valuable tool for teaching cell cycle regulation because they:
- Provide students with a hands-on, inquiry-based learning experience.
- Help students to develop a deeper understanding of the cell cycle and its regulation.
- Promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Encourage collaboration and teamwork.
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Cell cycle checkpoints are control mechanisms that ensure the accurate progression of the cell cycle. They are critical for maintaining genomic integrity and preventing the proliferation of damaged cells.
There are three main types of cell cycle checkpoints:
G1 Checkpoint
- Occurs at the end of G1 phase before the cell enters S phase.
- Checks for DNA damage, nutrient availability, and growth factor signals.
- If conditions are not favorable, the cell will either enter G0 phase or undergo apoptosis.
G2/M Checkpoint
- Occurs at the end of G2 phase before the cell enters mitosis.
- Checks for DNA damage and ensures that all chromosomes are properly aligned at the metaphase plate.
- If conditions are not favorable, the cell will either delay entry into mitosis or undergo apoptosis.
M Checkpoint
- Occurs during mitosis to ensure that chromosomes are properly separated and distributed to daughter cells.
- If conditions are not favorable, the cell will either delay anaphase or undergo apoptosis.
Factors Affecting Cell Cycle Regulation
Cell cycle regulation is a complex process that is influenced by a variety of factors. These factors can be either internal or external to the cell, and they can affect cell cycle progression in a variety of ways.
Internal Factors
Internal factors that can affect cell cycle regulation include the availability of nutrients, the presence of growth factors, and the cell’s own internal clock.
- Nutrients:The availability of nutrients can affect cell cycle progression. For example, if a cell is deprived of glucose, it will not be able to produce the energy it needs to divide, and cell cycle progression will be arrested.
- Growth factors:Growth factors are proteins that stimulate cell growth and division. When growth factors are present, they bind to receptors on the cell surface and trigger a cascade of events that lead to cell cycle progression.
- Internal clock:Cells have an internal clock that helps to regulate cell cycle progression. This clock is controlled by a group of genes called the cell cycle clock genes.
External Factors
External factors that can affect cell cycle regulation include the presence of toxins, radiation, and mechanical stress.
- Toxins:Toxins can damage DNA and other cellular components, which can lead to cell cycle arrest or cell death.
- Radiation:Radiation can also damage DNA and other cellular components, leading to cell cycle arrest or cell death.
- Mechanical stress:Mechanical stress, such as that caused by stretching or compression, can also affect cell cycle progression.
Manipulation of Cell Cycle Regulation
The factors that affect cell cycle regulation can be manipulated to control cell growth and division. For example, growth factors can be used to stimulate cell growth and division, while toxins can be used to inhibit cell growth and division.
The manipulation of cell cycle regulation is a powerful tool that can be used to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer and AIDS.
Cell Cycle Regulation and Cancer
Cell cycle regulation is crucial for maintaining tissue homeostasis and preventing the development of cancer. Dysregulation of cell cycle regulation can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation, a hallmark of cancer.
Cancer cells often exhibit defects in cell cycle checkpoints, allowing them to bypass normal growth control mechanisms. These defects can arise from mutations in genes encoding cell cycle regulators, such as tumor suppressor genes (e.g., p53, Rb) and oncogenes (e.g.,
cyclin D1, c-Myc).
Targeting Cell Cycle Regulation for Cancer Treatment, Pogil cell cycle regulation answers
Targeting cell cycle regulation is a promising strategy for cancer treatment. By inhibiting the activity of oncogenes or activating tumor suppressor genes, it is possible to restore normal cell cycle control and prevent uncontrolled cell growth.
- Checkpoint inhibitors:These drugs block cell cycle checkpoints, allowing damaged cells to undergo apoptosis (programmed cell death).
- CDK inhibitors:These drugs target cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), which are key regulators of cell cycle progression.
- mTOR inhibitors:These drugs inhibit the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a protein kinase that regulates cell growth and proliferation.
These treatments have shown promising results in clinical trials and are currently being used or investigated for the treatment of various types of cancer.
FAQ Resource
What is cell cycle regulation?
Cell cycle regulation refers to the intricate mechanisms that control the progression of cells through various stages of growth and division.
Why is cell cycle regulation important?
Cell cycle regulation ensures the proper growth, development, and function of organisms. Dysregulation of cell cycle regulation can lead to various diseases, including cancer.
What are the key components involved in cell cycle regulation?
Key components include cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and checkpoints that monitor the cell’s readiness to progress through the cell cycle.
