The immune system worksheet answers provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricate workings of your body’s defense mechanisms. This essential system protects us from infections, diseases, and foreign invaders, ensuring our overall health and well-being. Delve into the fascinating world of immunology as we explore the components, functions, and dysregulations of the immune system, empowering you with knowledge to maintain optimal immune health.
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from harmful substances. It recognizes and eliminates pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites, while also distinguishing between healthy and foreign cells.
1. Immune System Overview
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from infection and disease. It is responsible for recognizing and eliminating foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
There are two main types of immune responses: innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity is the body’s first line of defense and is present from birth. It includes physical barriers, such as the skin and mucous membranes, as well as chemical barriers, such as stomach acid.
Adaptive immunity is more specific and develops over time as the body is exposed to new pathogens. It involves the production of antibodies and the activation of specialized immune cells.
Common immune system disorders include allergies, autoimmune diseases, and immunodeficiencies.
2. Components of the Immune System
The key components of the immune system include:
- Cells:White blood cells, including neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes, and dendritic cells, are responsible for recognizing and eliminating pathogens.
- Tissues:Lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow are sites where immune cells are produced and activated.
- Organs:The thymus is responsible for the development of T lymphocytes, while the bone marrow produces all other types of blood cells.
These components work together to provide the body with a robust defense against infection.
| Cell Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Neutrophils | Phagocytosis of bacteria |
| Macrophages | Phagocytosis of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens |
| Lymphocytes | Antibody production and cell-mediated immunity |
| Dendritic cells | Antigen presentation to T lymphocytes |
3. Immune System Development and Function
The immune system develops throughout life, with the most significant changes occurring during childhood. Innate immunity is present at birth, while adaptive immunity develops as the body is exposed to new pathogens.
The immune system recognizes and responds to foreign invaders through a process called antigen recognition. Antigens are molecules that are present on the surface of pathogens. When an antigen is recognized by an immune cell, it triggers a cascade of events that leads to the elimination of the pathogen.
Vaccines and immunization play a crucial role in strengthening the immune system. Vaccines contain weakened or inactivated pathogens that stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies and activate immune cells. This allows the body to mount a rapid and effective response to future infections.
4. Immune System Dysregulation
Immune system dysregulation can occur when the immune system fails to function properly. This can lead to a variety of disorders, including autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiencies.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. Examples of autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis.
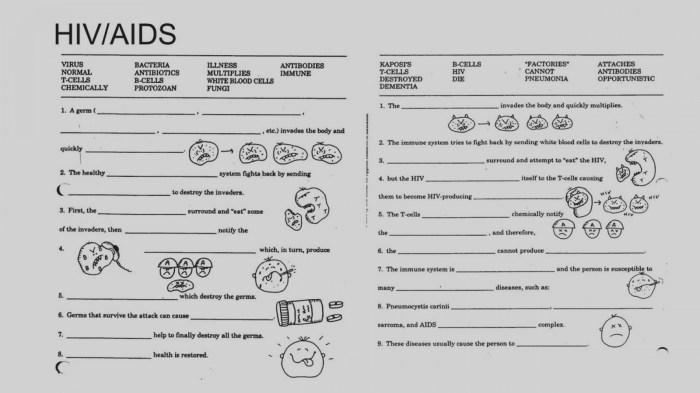
Immunodeficiencies occur when the immune system is unable to provide adequate protection against infection. Examples of immunodeficiencies include HIV/AIDS, severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), and common variable immunodeficiency (CVID).
Immune system dysregulation can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle.
5. Maintaining Immune System Health
There are a number of things you can do to maintain a healthy immune system, including:
- Eating a healthy diet:A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the body with the nutrients it needs to function properly.
- Getting regular exercise:Exercise helps to improve circulation and boost the production of immune cells.
- Managing stress:Stress can suppress the immune system, so it is important to find healthy ways to manage stress.
- Getting enough sleep:Sleep is essential for the immune system to function properly.
- Taking probiotics:Probiotics are live bacteria that can help to support the immune system.
- Avoiding smoking:Smoking damages the immune system and increases the risk of infection.
Questions Often Asked: The Immune System Worksheet Answers
What are the different types of immune responses?
There are two main types of immune responses: innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity provides immediate, non-specific defense against pathogens, while adaptive immunity develops over time and provides targeted protection against specific invaders.
What are some common immune system disorders?
Immune system disorders can arise due to various factors, including genetic defects, environmental triggers, and lifestyle choices. Some common disorders include autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiencies, and allergies.
How can I strengthen my immune system?
Maintaining a healthy immune system involves adopting healthy habits such as a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains; regular exercise; adequate sleep; and effective stress management techniques.